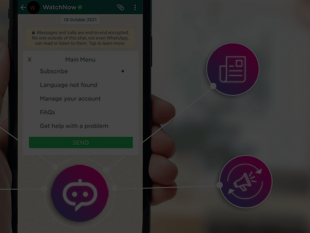
According to research from Gartner, around 70% of the global workforce will have interactions with a conversational system on a daily basis by 2022.
As a designer of such a conversational platform, you must think of it as putting a puzzle together. You must consider the technological limitations of your platform and craft what you want users to do within the space.
Bit by bit, use-case by use-case, you put the puzzle together with the end goal of creating conversations that feel natural, user-friendly, and intuitive.
In this article, we will discuss briefly how you can best use the tools available to you within the WhatsApp API to bring the conversation design to life.
1. Understanding your business requirements and audience
The most important step in designing a great conversational flow is defining a clear problem statement that the bot is intended to solve.
For example – “I need to design an automated customer support bot for my online shoe store.”
Once you have identified the overall problem statement, you should start to fill in the details by asking questions like
- What channels are customers currently using for support queries?
- What is the percentage of calls/emails/chat that customers currently use?
- What are the most common complaints?
- How are we generating leads currently?
- How well is our website/social media working for conversions?
2. Building a bot persona (researching your buyer)
To create the persona that the bot will communicate as, you must undertake comprehensive research to understand the practical details of what your customers really want. You should go to internet forums, app store reviews, the comments section on your social media and your reviews to understand what language your customers are using and what their questions are.
If you are already using a CRM, you need to know what the average turnaround time is for currently resolving tickets. How many customer agents do you currently have, and when are they active? Once you collate this information, you can start creating a bot persona.
For example, if you are a fitness brand your average customer might be young, financially independent individuals. To cater to them, your brand persona should be that of a young, enthusiastic fitness guru rather than an old, world-weary advisor.
Use this persona to role-play conversations with your customers. You will see that there is a lot of different conversational situations that could come up and the bot must be able to deal with emotions, technical jargon, and even separate languages. It should be able to speak to the angriest and the shyest customer and guide them towards a conversion.
3. Picking the right words (affirmations, ice breakers, sign off phrases)
To keep the conversation flowing and natural, it is important that you pick the right words and phrases to move the user along their journey.
Broadly speaking, your bot persona will fall into one of these three categories
- Formal (Professional, minimalistic, and helpful tone)
- Casual (Friendly and helpful)
- Quirky (Energetic, funny, and niche-specific)
Conversations are inherently very contextual, so consider these as guidelines and not strict rules when you are designing your bot. Let us consider a few use-cases.
1. Acknowledgement of user query
Formal response – “Definitely / Understood”
Casual response – “Happy to help / Glad you asked!”
Quirky response – “Gotcha / Sure thing”
1. Acknowledgement of user query

Formal response – “Definitely / Understood”
Casual response – “Happy to help / Glad you asked!”
Quirky response – “Gotcha / Sure thing”
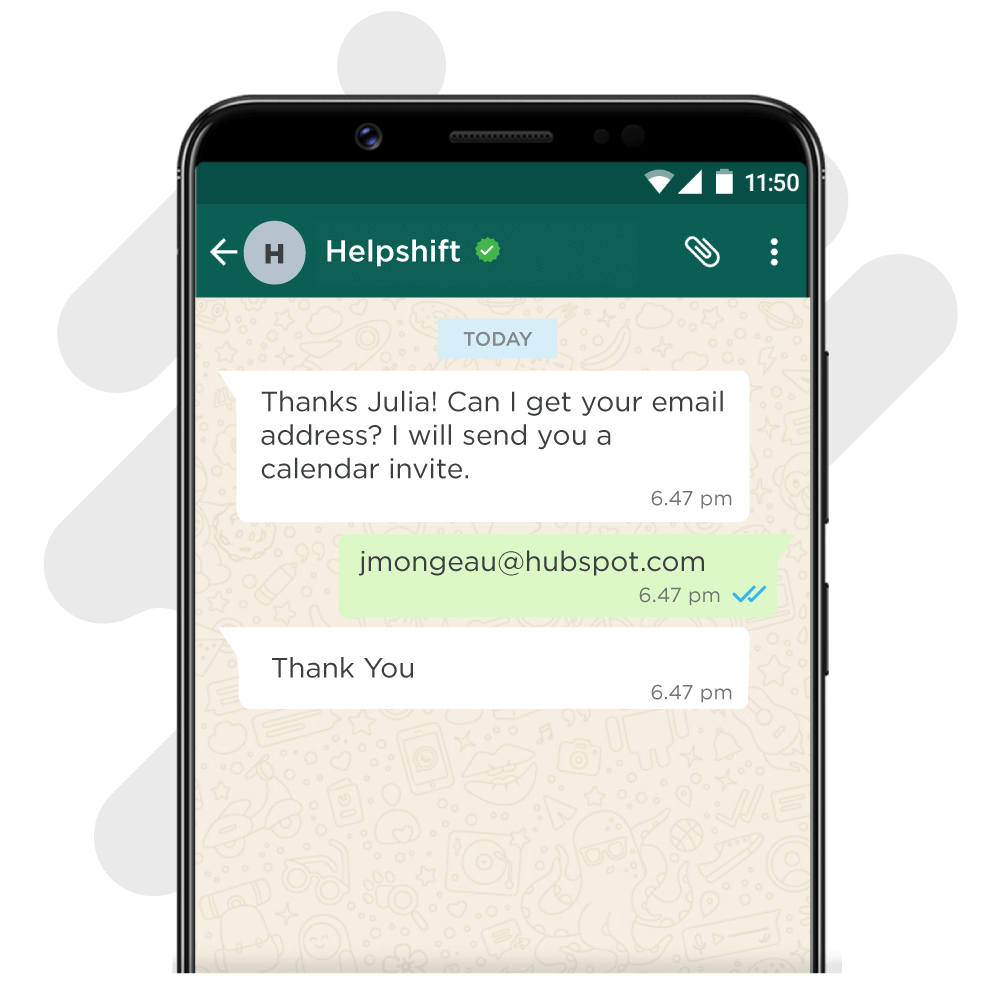
2. After user information has been collected
Formal response – “Noted / Thank You”
Casual response – “Perfect / All set!”
Quirky response – “Okay cool / Mission accomplished”
2. After user information has been collected

Formal response – “Noted / Thank You”
Casual response – “Perfect / All set!”
Quirky response – “Okay cool / Mission accomplished”
3. When you want to collect information, engage the user and move the conversation along
Formal response – “Before we begin / Next step”
Casual response – “We’re almost there / Just one more step”
Quirky response – “I’d like to know you better”
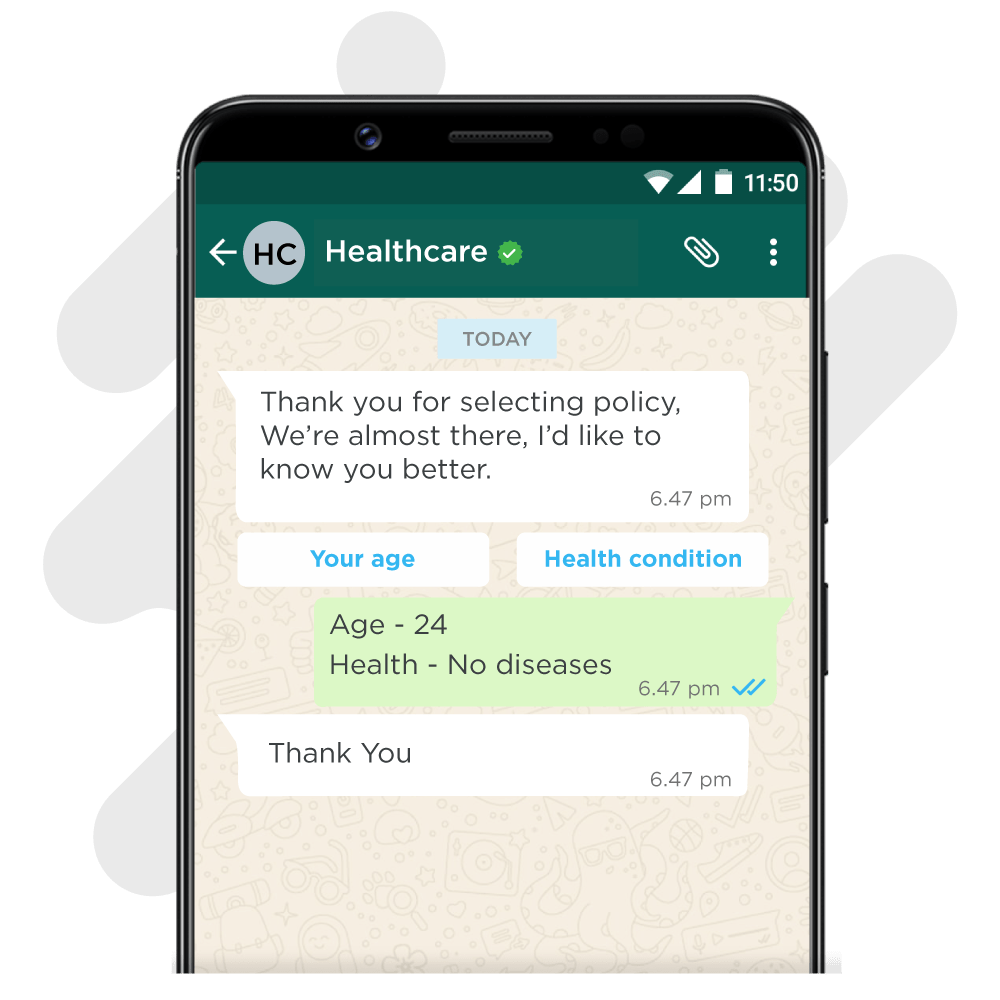
3. When you want to collect information, engage the user and move the conversation along

Formal response – “Before we begin / Next step”
Casual response – “We’re almost there / Just one more step”
Quirky response – “I’d like to know you better”
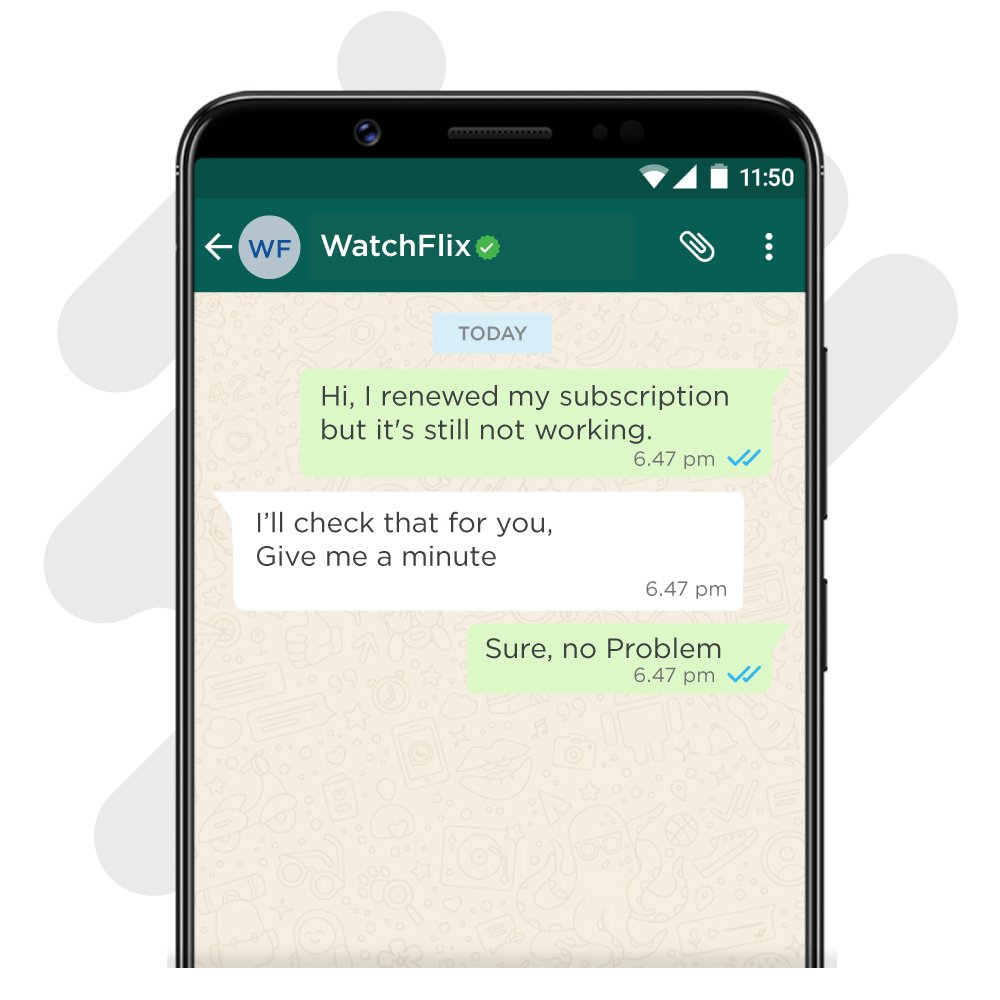
4. Asking the user to wait
Formal response – “Give me a minute / One moment”
Casual response – “Hang on… / Hold up a second”
Quirky response – “Stay right here / On it, boss”
4. Asking the user to wait

Formal response – “Give me a minute / One moment”
Casual response – “Hang on… / Hold up a second”
Quirky response – “Stay right here / On it, boss”
5. Ending the conversation
Formal response – “Happy to have helped / Is there anything else I can help with?”
Casual response – “I’ll be here if you need me / You know where to find me if you need help”
Quirky response – “Toodles / Twas a pleasure helping you!”
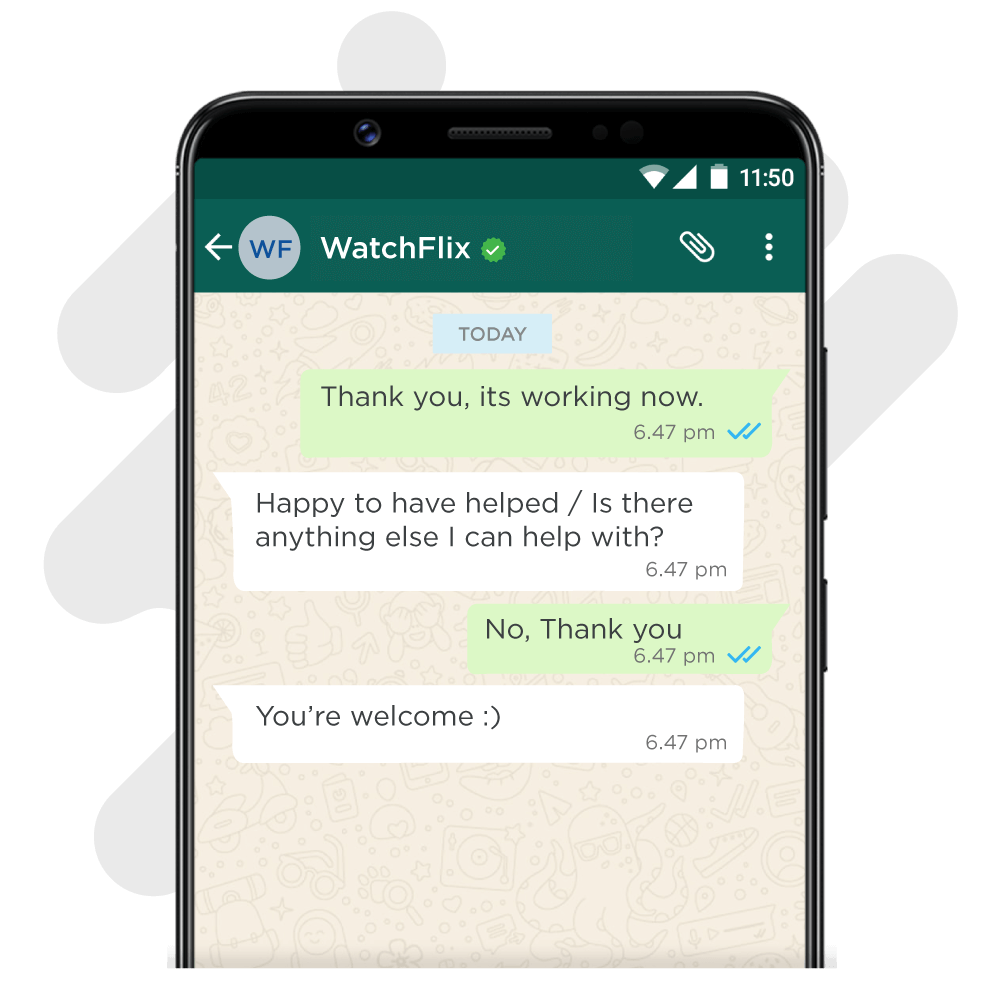
5. Ending the conversation

Formal response – “Happy to have helped / Is there anything else I can help with?”
Casual response – “I’ll be here if you need me / You know where to find me if you need help”
Quirky response – “Toodles / Twas a pleasure helping you!”
4. Choosing the right elements (QR/Buttons/Carousels/Location picker etc.)
Depending on the context and where you are in the conversation, you might pick a textual or a graphical response such as images or buttons.
Let us take a look at some of the elements you can use while designing your conversation.
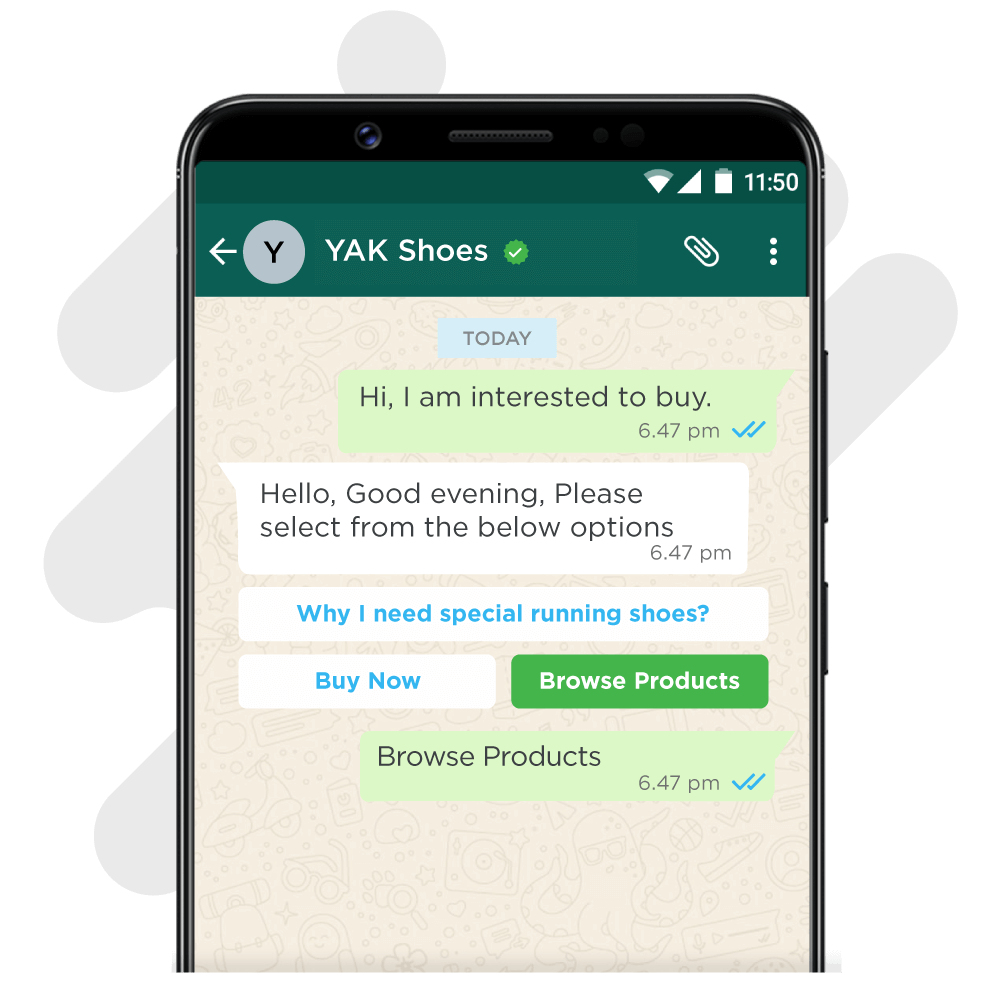
1. Quick Replies
These are tappable buttons that the user can use to reply instead of typing out a whole sentence or phrase. These are extremely common and should be used to lead the user into the next phase of the conversation.
For example, for your online shoe store, you might have quick replies like “Browse Products” or “Why do I need special running shoes?”
1. Quick Replies

These are tappable buttons that the user can use to reply instead of typing out a whole sentence or phrase. These are extremely common and should be used to lead the user into the next phase of the conversation.
For example, for your online shoe store, you might have quick replies like “Browse Products” or “Why do I need special running shoes?”
2. Away messages
Away messages can be used to convey that you are busy or currently out of office. You can set your business hours within the WhatsApp Business API and choose to send the messages either all the time, or outside of your specified business hours.

2. Away messages

Away messages can be used to convey that you are busy or currently out of office. You can set your business hours within the WhatsApp Business API and choose to send the messages either all the time, or outside of your specified business hours.
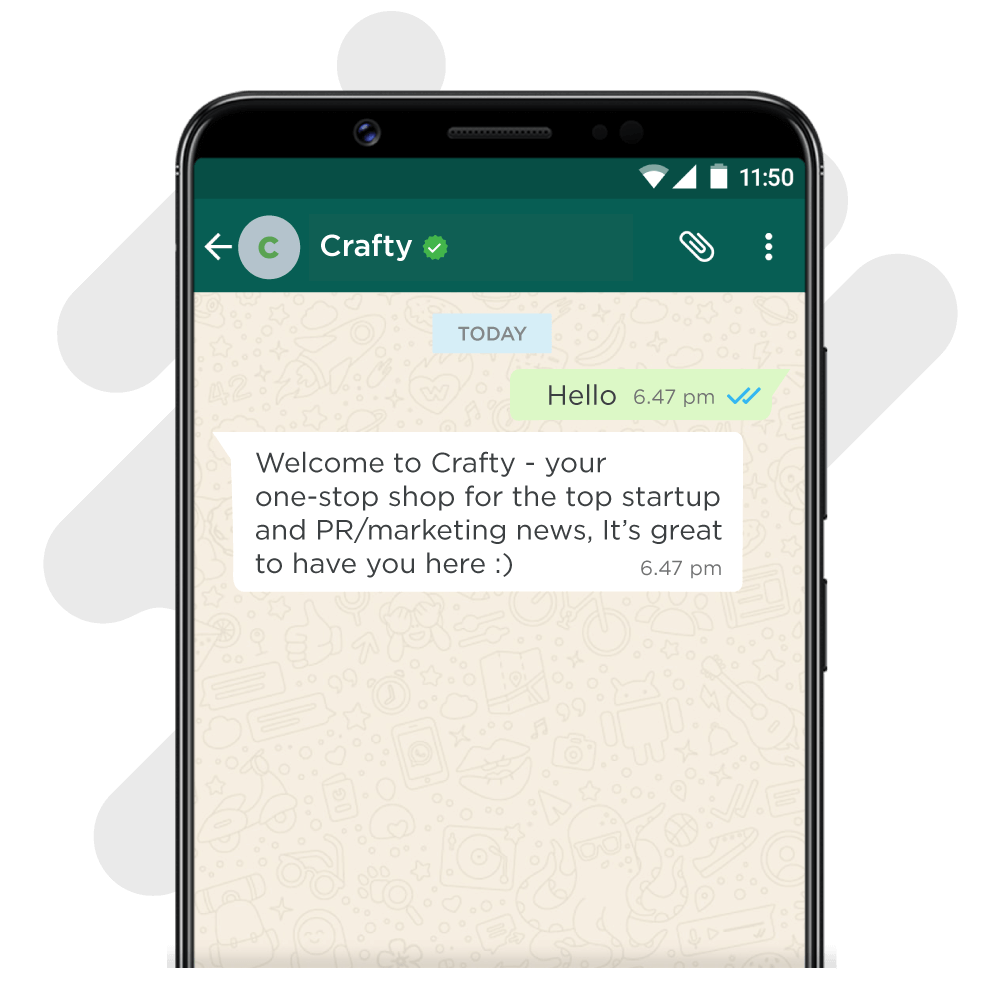
3. Greeting messages
These are used when a user first initiates a conversation with you. These need to be representative of the vibe you want to project as a brand (business-casual/ friendly/ quirky).
To give the user an optimal experience, make sure these greetings match the overall tone you are going for and convey wit and personality.
3. Greeting messages

These are used when a user first initiates a conversation with you. These need to be representative of the vibe you want to project as a brand (business-casual/ friendly/ quirky).
To give the user an optimal experience, make sure these greetings match the overall tone you are going for and convey wit and personality.
4. List Messages
Text-only messages can devolve into a wall of text if you are using them to convey a long list of options. This is where List Messages come in to provide a quick and easy bridge for customers to move to the next step of their journey.
List messages can be used in situations where you want to present the user with several options, such as
- They need to book an appointment
- They need to choose specific seats for an event they are attending
- Menu options depending on user input
- They need to locate the closest outlet or store
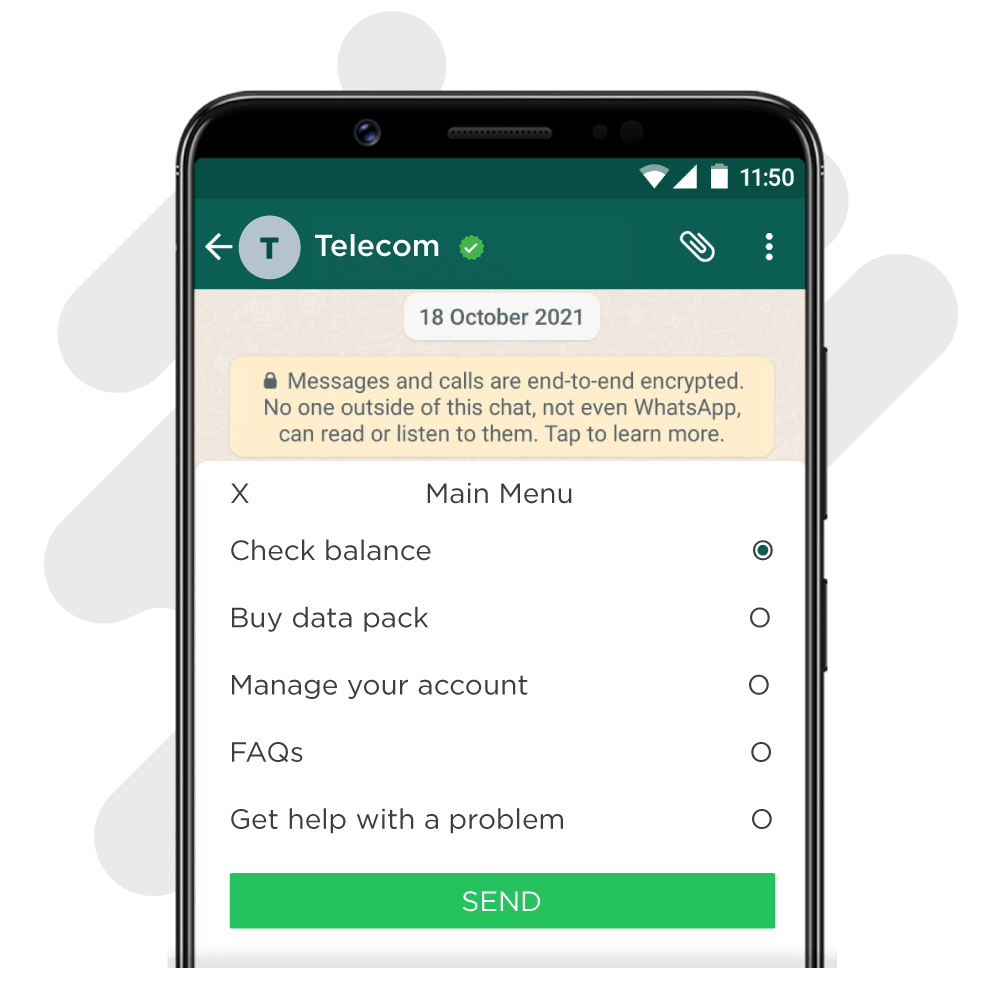
4. List Messages

Text-only messages can devolve into a wall of text if you are using them to convey a long list of options. This is where List Messages come in to provide a quick and easy bridge for customers to move to the next step of their journey.
List messages can be used in situations where you want to present the user with several options, such as
- They need to book an appointment
- They need to choose specific seats for an event they are attending
- Menu options depending on user input
- They need to locate the closest outlet or store
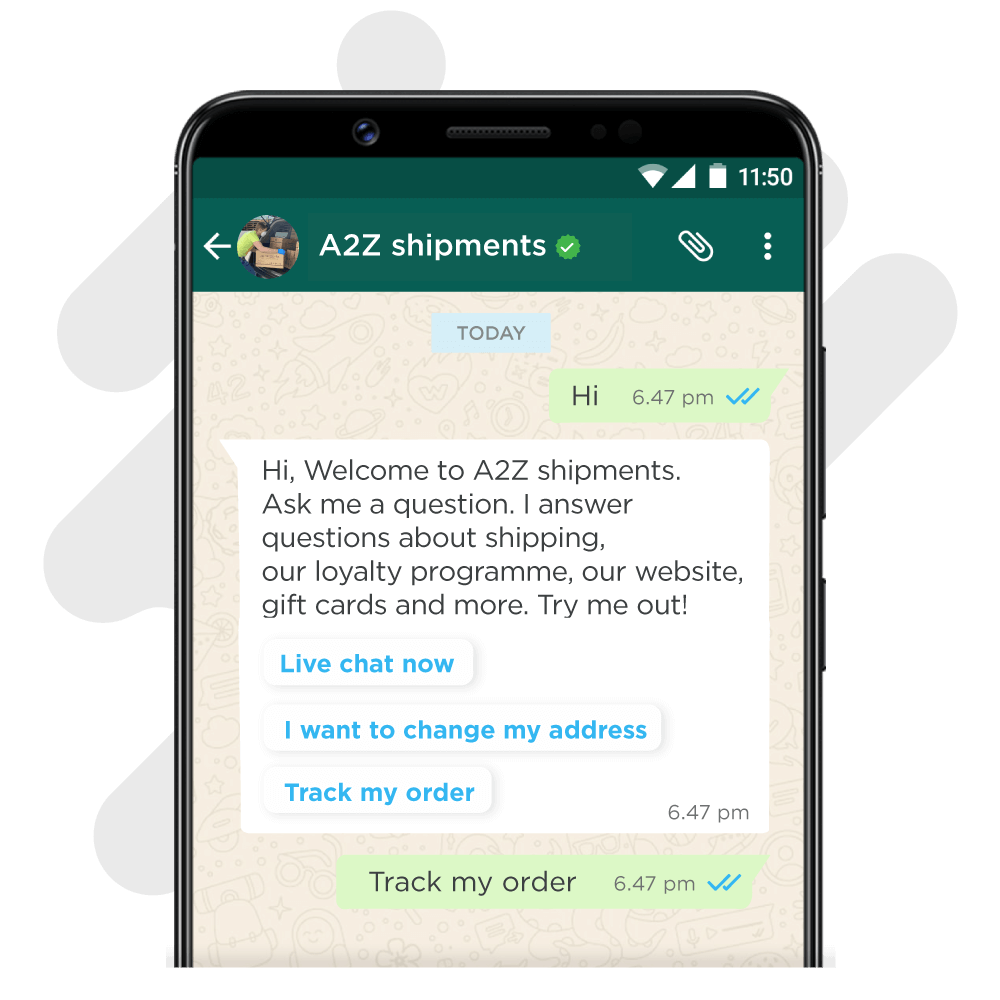
5. FAQs
Adding the most commonly asked questions to your bot is a great way to ensure that most people will have their questions answered without needing to involve an actual customer service agent.
Make sure that all of the FAQ sections move the user forward naturally in the conversation. If a particular answer is too lengthy, consider creating a video or image that can convey a majority of the information.
5. FAQs

Adding the most commonly asked questions to your bot is a great way to ensure that most people will have their questions answered without needing to involve an actual customer service agent.
Make sure that all of the FAQ sections move the user forward naturally in the conversation. If a particular answer is too lengthy, consider creating a video or image that can convey a majority of the information.
Always begin with the end in mind and prioritize the most common use cases. Once you have your brand persona set, you should begin testing and mapping out different variations of user journeys with the bot. By testing the bot in distinct scenarios, you will be able to iron out edge cases and roadblocks.
Designing an intuitive conversational flow can mean the difference between a massively successful campaign and a mediocre one. To learn more about building memorable user experiences with WhatsApp, make sure you bookmark our blog and visit regularly!